Alternative aquafeed needs ‘complementary’ approach

There is no single solution to finding alternative protein sources for aquafeed, according to a study into options for reducing the sector’s dependence on marine ingredients.
The study, published this week in the academic journal Reviews in Fisheries Science and Aquaculture, was led by led by Dr Brett Glencross Technical Director at the marine ingredients organisation IFFO, and a cohort of international fish nutritionists.
The review considers a large variety of protein sources used in aquafeeds: marine ingredients (produced from either forage fishery or by-products from both fishery and aquaculture resources), processed animal proteins (made from terrestrial animals produced for human consumption from which by-products are generated, and also insect and worm meals), single-cell protein resources (produced from bacterial, yeast, fungal, or microalgal origins), grain protein sources (making up the largest volume of all global aquafeeds) such as cereals, oilseeds, pulses, including those plant resources used either unmodified, or with varying degrees of processing.
Dr Glencross said: “The assessment demonstrates that every ingredient has strengths and weaknesses. In many cases, the weaknesses of one ingredient can be matched with the strengths of other ingredients to identify opportunities for complementarity.”
For example, he explained, soybean has the scale and stability of supply and consistency of product quality but lacks palatability for many species. Fishmeal is limited in supply but has excellent palatability characteristics. They both work well with each other in a highly complementary nature.
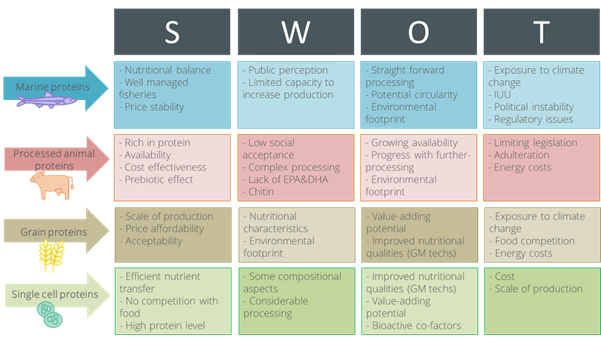
Alternative proteins for aquafeed: SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) table.
The study’s key recommendations for the industry are:
- improve management of existing resources to increase their productivity;
- ensure nothing is wasted; and
- further develop non-competing resource production.
Glencross added that an important observation from the review was that “…by better appreciating the positives and negatives of each ingredient, it becomes possible to increase our adaptability in responding to the various opportunities for their use in feeds and improve our sustainability of the sector moving forward”
Overall, while technical progress in working with an increasing range of ingredients is making clear headway, the scale-up of new resources to delivering meaningful volumes still needs work.
Glencross, B., Ling, X., Gatlin, D., Kaushik, S., Øverland, M., Newton, R., & Valente, L. M. (2024). A SWOT Analysis of the Use of Marine, Grain, Terrestrial-Animal and Novel Protein Ingredients in Aquaculture Feeds. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 1-39.

